Page 36 - _NIPER-G Annual Report 2019-201
P. 36
Research Area -2
Design and Biological Evaluation of Lipoprotein-Based Donepezil Nanocarrier
for Enhanced Brain Uptake through Oral Delivery
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder associated with
memory and cognitive impairment. Donepezil is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used for the
symptomatic treatment of AD. However, high dose of donepezil is prescribed to achieve
effective concentration in the brain, which leads to significant side effects, gastrointestinal
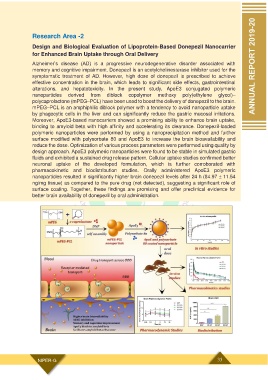
alterations, and hepatotoxicity. In the present study, ApoE3 conjugated polymeric
nanoparticles derived from diblock copolymer methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)–
polycaprolactone (mPEG–PCL) have been used to boost the delivery of donepezil to the brain.
mPEG–PCL is an amphiphilic diblock polymer with a tendency to avoid nanoparticle uptake
by phagocytic cells in the liver and can significantly reduce the gastric mucosal irritations.
Moreover, ApoE3-based nanocarriers showed a promising ability to enhance brain uptake,
binding to amyloid beta with high affinity and accelerating its clearance. Donepezil-loaded
polymeric nanoparticles were performed by using a nanoprecipitation method and further
surface modified with polysorbate 80 and ApoE3 to increase the brain bioavailability and
reduce the dose. Optimization of various process parameters were performed using quality by
design approach. ApoE3 polymeric nanoparticles were found to be stable in simulated gastric
fluids and exhibited a sustained drug release pattern. Cellular uptake studies confirmed better
neuronal uptake of the developed formulation, which is further corroborated with
pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies. Orally administered ApoE3 polymeric
nanoparticles resulted in significantly higher brain donepezil levels after 24 h (84.97 ± 11.54
ng/mg tissue) as compared to the pure drug (not detected), suggesting a significant role of
surface coating. Together, these findings are promising and offer preclinical evidence for
better brain availability of donepezil by oral administration.
NIPER-G 33