Page 73 - _NIPER-G Annual Report 2019-201
P. 73
fructose diet caused cardiac dysfunction along with insulin resistance. They
demonstrated that vitamin D deficiency in rats resulted in cardiac contractile
dysfunction and was linked to myocardial insulin resistance, a recognized predecessor
of heart failure. The findings in vitamin D deficient diet-fed animals were compared to
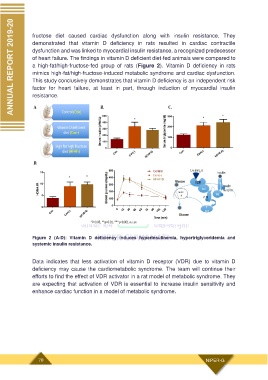
a high-fat/high-fructose-fed group of rats (Figure 2). Vitamin D deficiency in rats
mimics high-fat/high-fructose-induced metabolic syndrome and cardiac dysfunction.
This study conclusively demonstrates that vitamin D deficiency is an independent risk
factor for heart failure, at least in part, through induction of myocardial insulin
resistance.
Figure 2 (A-D): Vitamin D deficiency induces hyperinsulinemia, hypertriglyceridemia and
systemic insulin resistance.
Data indicates that less activation of vitamin D receptor (VDR) due to vitamin D
deficiency may cause the cardiometabolic syndrome. The team will continue their
efforts to find the effect of VDR activator in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. They
are expecting that activation of VDR is essential to increase insulin sensitivity and
enhance cardiac function in a model of metabolic syndrome.
70 NIPER-G