Page 72 - _NIPER-G Annual Report 2019-201
P. 72
of p53 at lysine 381 (K381), which is a binding site for MDM2, a p53 inhibitor. MDM2
binds at K381 to inhibit the p53 nuclear translocation. However, when p53 is acetylated
at K381, MDM2 fails to bind p53 and hence results in increased nuclear translocation
of the protein, and thereby enhanced p53-dependent apoptosis. Increased
cardiomyocyte loss due to apoptosis is responsible for fibrosis. The data showed that
SIRT2 over expression significantly reduced p53 acetylation and inhibited apoptosis
in H9c2 cells.
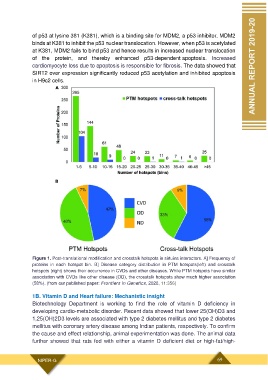
Figure 1. Post-translational modification and crosstalk hotspots in sirtuins interactors. A] Frequency of
proteins in each hotspot bin. B] Disease category distribution in PTM hotspots(left) and crosstalk
hotspots (right) shows their occurrence in CVDs and other diseases. While PTM hotspots have similar
association with CVDs like other disease (OD), the crosstalk hotspots show much higher association
(58%). (from our published paper: Frontiers in Genetics, 2020, 11:356)
1B. Vitamin D and Heart failure: Mechanistic insight
Biotechnology Department is working to find the role of vitamin D deficiency in
developing cardio-metabolic disorder. Recent data showed that lower 25(OH)D3 and
1,25(OH)2D3 levels are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes
mellitus with coronary artery disease among Indian patients, respectively. To confirm
the cause and effect relationship, animal experimentation was done. The animal data
further showed that rats fed with either a vitamin D deficient diet or high-fat/high-
NIPER-G 69